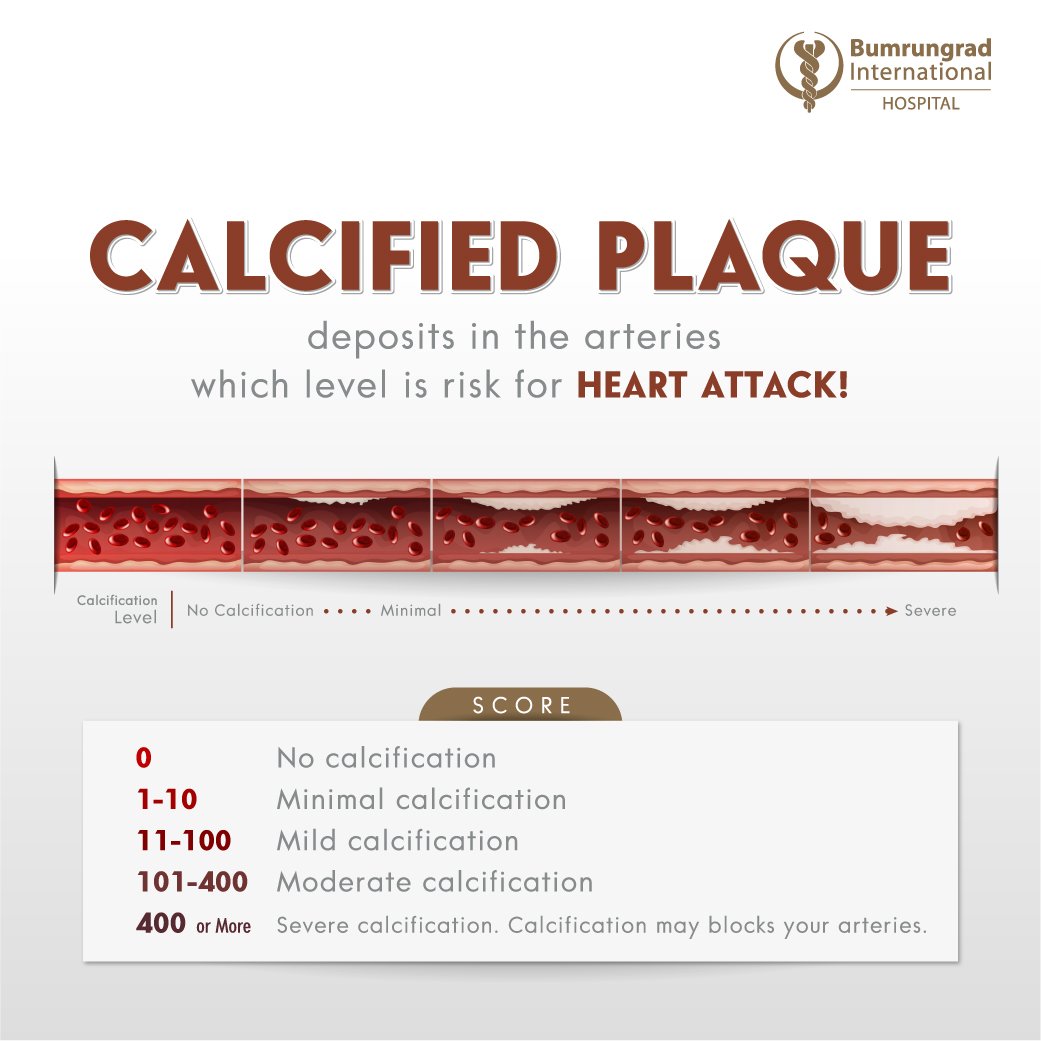
‘Plaque’ is made up of excess cholesterol, calcium, and other substances in the blood. Over time, plaque builds up in the walls of the arteries, causing the narrowing of the blood vessels. This may increase the risk of coronary artery disease, as well as related health conditions such as sudden heart attack.
Measuring the amount of calcified plaque in your coronary arteries is vital.
Calcium Scoring CT measures the amount of calcified plaque in your coronary arteries through a CT Scan, that provides scores ranging from 0 to over 400. The test helps doctors to calculate the risk of developing coronary artery disease, and provide recommendations for a suitable treatment plan.
CT scan scoring :
Score 0: Low risk of heart attack
Scores 1 – 10: Less than 10% chance of experiencing a heart attack
Scores 11 – 100: Moderate risk of heart attack; doctor may recommend lifestyle changes
Scores 101 – 400: Moderate to high risk of heart attack; doctor may recommend treatment through medication
Scores > 400: High risk of heart attack; doctor may recommend beginning treatment right away
Remarks
*The score reflects the total area of calcium deposits within the coronary arteries.
** This test is not recommended for evaluating soft plaque deposits in the coronary arteries.
For more information please contact:
Last modify: April 30, 2025